HYBRIDISATION TECHNIQUES:
- it means when a single stranded DNA binds to complementary sequence with the same base base pairing rules.
- thus used to detect the presence and amount of complementary DNA sequence present in isolated DNA
- for detection PROBES are used
- Probes are relatively small stranded sequences of DNA that recognize and bind to complementary sequences
- for visualization probes are tagged with a fluorescent label (which can be seen under UV) or tagged with radioactive label by a technique called autoradiography (visualized under photographic film)

FLUORESCENT LABEL PROBES:


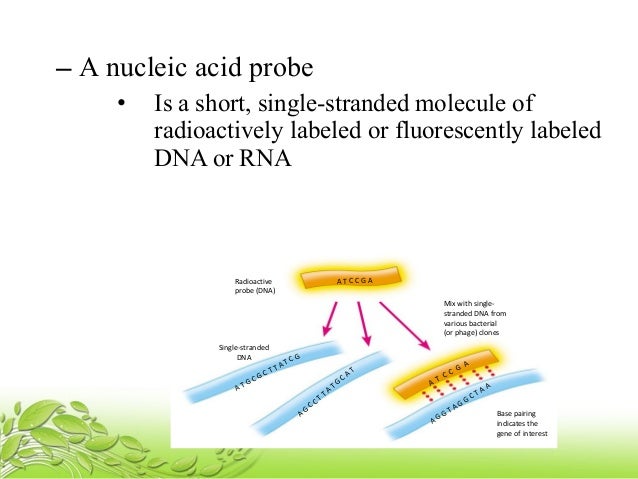
This principle of hybridization is used in our next topic i.e. SOUTHERN HYBRIDIZATION:
This was invented by E.M.Southern in the year 1975
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XEWu78qNcIg
Remember 2 words here that are blotting and baking
There are different types of blotting techniques as: SOUTHERN BLOT, NORTHERN BLOT AND WESTERN BLOT
Southern blots - DNAs are transfered to paper and specific nucleotide sequences are detected. Northern blots - RNAs are transfered to paper and specific nucleotide sequences are detected. Western blots - Proteins are transfered to paper and specific proteins are detected by using antibodies.

No comments:
Post a Comment