IIn the words of an ex student (KULDEEP SHARMA)
I knew that I would
opt for science in class 11. The problem, however, was to choose the fourth and
fifth subjects. I was sure that I would not take biology since I love
mathematics. I choose biotechnology as the fifth subject, oblivious to what it
entails.
Biotechnology is a
highly interdisciplinary subject. It includes biochemical engineering, life
science, genetic engineering, material science, and bioinformatics: it goes
beyond biology. Learning these basic concepts in class 11 and 12 provides a
template to continue for higher studies in the same field. I enjoyed learning
the subject, and never imagined that I would spend my next seven years in the
same area.
The 21st century
belongs to biology since the field is relatively unexplored. Recent Nobel
Prizes have been conferred to work mostly related to biology. Biotechnology is
the most expensive laboratory in any academic institution. Researchers from
disparate backgrounds are now incorporating some aspect of biology in their
research work. In India, the Department of Biotechnology is a separate
department under the Ministry of Science & Technology.
Recent advancements in
the field have led to several breakthroughs. A newly developed system -
CRISPR-Cas9 - is a gene-editing tool that allows DNA to be added, removed, or
modified at particular locations. DNA based data storage devices are a new
reality. In June 2019, scientists encoded all 16 GB text from Wikipedia’s
English-language version into the synthetic DNA. The unprecedented COVID-19
pandemic has led everyone to realize the importance of this field. Detection
kits, vaccines, and antibodies find their place in contemporary public
discourse.
The biotechnology
sector is growing at a rate of 12% over the last five years, with a turnover of
₹28,185 crores in 2014-15. By the end of 2025, it will touch the $100 billion
mark in India. The career prospects are bright, but it requires immense effort.
You can become whatever you love to: researcher, data scientist, academician, pedagogue,
intellectual property agent, science journalist, scientific advisor, forensics
expert, and entrepreneur.
About the author:
Kuldeep is pursuing
M.Tech. in Biological Engineering at IIT Gandhinagar. He is yet to submit the
Master’s Thesis.
NOW WE SHOULD KNOW ABOUT
BIOTECHNOLOGY:
Biotechnology is the exploitation of
biological processes for industrial and other purposes, especially the genetic
manipulation of microorganisms for the production of antibiotics, hormones,
etc.
Or simply we can say, In biotechnology, living organisms
are used to make useful chemicals and products or to perform an industrial
task.
Biotechnology is the field of science that involves the use of living things in
various fields as engineering, technology, medicine etc.
People still think that biotechnology is only about biology. But that is not it
seems to be. Knowledge of mathematics adds up to be an important to make your
career in this field.
Thus, I can say biotechnology as 5th subject with SCIENCE even with MATHEMATICS
is a good combination or we can say is a need of hour.
AFTER 12TH:
- B.TECH(BIOTECHNOLOGY)
- B.TECH (FOOD
TECHNOLOGY)
- B. TECH (DAIRY
TECHNOLOGY)
- B.TECH
(BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING)
- B.TECH
(AGRICULTURAL ENGINEERING)
- B.TECH
(ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING)
- B.TECH
(BIOINFORMATICS)
- B.SC.(BIOTECHNOLOGY)
- B.SC.
(BIOCHEMISTRY)
- B.SC.
(MICROBIOLOGY)
ELIGIBLE TO APPEAR IN
NEET: NATIONAL ELIGIBILITY CUM
ENTRANCE TEST for admission to MBBS/BDS Courses
These
are among lesser known fields of engineering which are in great demand in
present scenario. These courses are offered by few government institutes and
due to less awareness the students are not able to take the full benefit.
B.TECH (DAIRY TECHNOLOGY): NDRI, KARNAL, HARYANA
MPUAT, UDAIPUR RAJASTHAN
UNI. OF AGRICULTURE AND
TECHNOLOGY, KANPUR,UP
B.TECH (FOOD TECHNOLOGY): IIT, KHARAGPUR
NIT, ROURKELA
OSMANIA UNIVERSITY, HYDERABAD
B.TECH (BIOTECHNOLOGY): MOST OF THE IITS
DELHI TECHNOLOGICAL
UNIVERSITY, DELHI
NIT, WARANGAL
BITS, PILANI
B.TECH (ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING): IIT KHARAGPUR
MNIT, JAIPUR
And,
thus the list goes on ..........................
A
DETAILED LIST IS ATTACHED BELOW
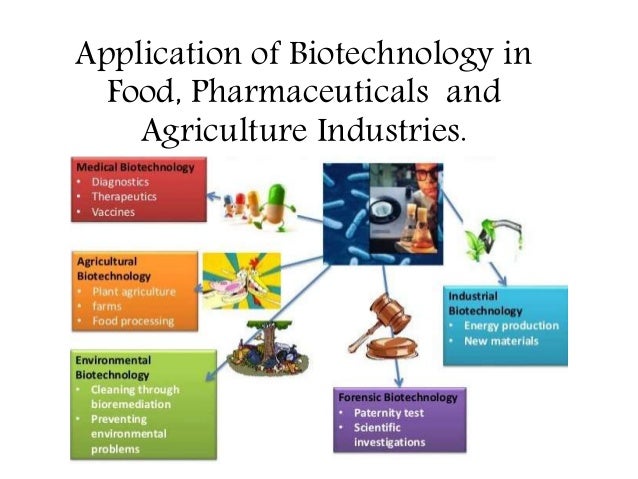
Now, we should discuss about the CAREER IN BIOTECHNOLOGY:
A number
of factors determine the demand of professionals from this interdisciplinary
field.The applications of this branch of science are vast and simply
mind-boggling. On one hand, it caters to the industrial sector such as food and
beverages industry, textiles industry, biological products, medicines and
pharmaceuticals while on the other hand this branch of science caters to the
requirements of agriculture, animal husbandry, nutrition and environmental
conservation. The list is a long and an envious one.
Although,
the name may suggest that this branch of science is steeped in biology but this
is not the case. Apart from biology, this branch of science also assimilates
diverse subjects like physics, chemistry and mathematics. Furthermore,
engineering applications are also an integral constituent of biotechnology.
Step-by-Step
In
opting for a specialised profession such as biotechnology, you must plan your
career right from your school days. In this context, the combination of
subjects of study at the 10+2 level must primarily include Biology, Chemistry,
Physics and even Mathematics. Among all
you are at edge that you can opt this subject at class 11. Once you have
finished schooling you can opt for a suitable undergraduate program (BSc, BE,
BTech) in Biotechnology from various academic institutions spread across the
country. The duration of a BSc program in biotechnology is three years whereas
it is four years for BE and BTech courses.
TOP
INSTITUTE / COLLEGES OFFERED BIOTECHNOLOGY COURSES IN INDIA
- Indian Institute of
Technology (Kharagpur,Madras,Guwahati and
Roorkee((www.iitkgp.ernet.in,www.iitm.ac.in)
- Anna
University,Chennai(www.annauniv.edu)
- Delhi
University,Delhi(www.du.ac.in)
- Manipal
University,Manipal(www.manipal.edu)
- VIT University
,Vellore(www.vit.ac.in)
- Padmashree Dr D Y Patil
Institute for Biotechnology and Bioinformatics,Navi Mumbai,(www.dypatil.com)
- Dr D Y Patil University
,Pune (www.dyoatiluniversity.org)
- SRM
university(www.srmuniv.ac.in)
Top Companies
Some
companies to work with:
1.
Biocon
2.
Serum Institute of India
3.
Panacea Biotech
4.
Mahyco Monsanto Biotech
5. Rasi
Seeds
6. Novo
Nordisk
7.
Aventis
8.
Indian Immunologicals
9.
Venkateshwara Hatcheries
10.
Ranbaxy
11. Dr.
Reddy’s Labs
12.
Piramal Healthcare.
Overall,
these are some of the major names in Indian biotechnological industry which
extensively use biotechnological processes and techniques to develop and
innovate products and processes.
IN THE NEAR FUTURE YOU WOULD BE:
Agricultural
and Food Scientist
The
Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) combines three related careers under the
heading of agricultural and food scientist: animal scientist, food scientist
and technologist, and soil and plant scientist. Although all have the ultimate
task of improving farm productivity, they accomplish this in different ways.
Agricultural
Engineer
Many
people don’t think of farming as being sophisticated. Seeds are planted, crops
are watered, and eventually food is harvested. But it is an extraordinarily
advanced field, and the largest farms are essentially food factories. Engineers
are involved in research and development as well as manufacturing. They might
oversee water supply and usage, design comfortable areas for the animals, and
create machines that can efficiently harvest crops with minimal food loss.
Agricultural engineers spend their time both in offices designing systems and
on farms testing and applying those systems.
Animal
Scientist
Farm
animals can be crossbred to produce better quality meat, eggs or milk. They can
also be bred to live longer, healthier lives, saving farmers money. Animal
scientists have the expertise in genetics and reproduction to crossbreed
effectively so that farmers can increase production and lower costs.
Biochemist and
Biophysicist
These
scientists spend most of their days in large laboratories researching how
living things function. They plan experiments; work directly with protein,
enzymes and DNA; and study the effect of external substances on living things.
Those who work for biotechnology companies or divisions work in applied
research, meaning they are looking to use their findings to solve a specific
problem. For instance, in the past, biochemists in agriculture have used
applied research to genetically modify rice to have more beta-carotene and, by
extension, vitamin A. This rice could be used in parts of the world where rice
was a staple food but vitamin A deficiency was a major killer. Biophysicists
working for energy companies, meanwhile, have made advances in developing fuel
such as ethanol from plants.
Biomedical
Engineer
These
product-makers either create tools to analyze medical problems or design tools
that improve patients’ lives. For instance, they can create better microscopes
or newer imaging technologies. More pertinent to the field of biotechnology,
however, is their work to create artificial limbs that respond to brain signals
or the recent invention of a bionic pancreas that eliminates the need for
insulin injections in people with diabetes.
Microbiologist
Microbiologists
research bacteria, viruses, fungi, algae and parasites — basically anything too
small to be seen with the naked eye. The field is highly specialized, meaning
that most microbiologists focus on studying just one type of microorganism. In
the context of biotechnology, microbiologists might work in the manufacturing
side of the industry, making sure that products are not contaminated, but they
are just as likely to be involved in research and development. The Bureau of
Labor Statistics Occupational Outlook Handbook provides the following example:
“They may study the use of microbes to clean up areas contaminated by heavy
metals or study how microbes could aid crop growth.”
REPUTED
DEPARTMENTS OF INDIA THAT ACCOMMODATE BIOTECHNOLOGISTS :
- BUREAU OF
POLICE (R&D)
- DRDO
- MINISTRY OF
AYUSH RESEARCH FELLOWSHIP
- BARC PRACTICAL
TRAINING PROJECT WORK
- NATIONAL
CENTRE FOR CELL SCIENCES
Biotechnology
is an emerging field and the day is not so far that the world will be conquered
by it, leaving behind the field of IT. So don’t confine yourself with the
feeling of Biotechnology having no scopes. Biotechnology is beyond biology and
is having a good scope in the field of R&D, Quality Control, and
Administration. The field is growing at a good pace and still, there is a long
way to go.
BIOTECHNOLOGY
COLLEGES AND COURSES IN INDIA
Name Of Colleges/Institution
|
Course
|
Eligibility
|
Duration
|
All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi .
Website: www.aiims.ac.in or www.aiims.edu
|
B.Tech Biotechnology
|
Class XII with Physics, Chemistry and Biology.
Entrance test
|
4 years
|
GGS Indraprastha University , Delhi .
Website: www.ipu.ac.in.
|
B.Tech /M.Tech Biotechnology [Dual Degree]
|
10+2 with 55% marks in Physics Chemistry and Biology & Maths.
|
5½ years
|
Indian Institute Of Technology , New Delhi -110016.
Website: iitd.ac .in
|
M.Tech- Integrated 5yrs Dual Degree, Biochemistry Engg.&
Biotechnology
|
Physics, Chemistry & Maths in XII are eligible.
|
5 yrs
|
|
|
B.Tech /M.Tech Biotechnology Dual Degree.
|
Physics, Chemistry & Maths in XII are eligible
|
5 ½ years
|
Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur, West Bengal .
Website: iitkgp.ernet.in
|
M.Tech Biotechnology Integrated- 5½ years
|
Class XII with Physics, Maths Chemistry & Biology.
|
5½ years
|
University Of Rajasthan , Jaipur.
Website:www.uniraj.org
|
1] B.Tech /M.Tech Biotechnology
Integrated.
2] B.Sc[Hon] Biotechnology
|
1] 10+2.
Entrance test of PET
2] Class XII [Sciences.]
|
3 years
|
Punjab University , Chandigarh .
Website: www.puchd.ac.in or www.pec.ac.in
|
BE. Biotechnology
|
10+2 with 60% in Physics, Chemistry & Maths.
Admission through AIEEE
|
4years
|
Shri Mata Vaishno Devi University.
Website:www.smvdu.org
|
B.Tech [Industrial Biotechnology
|
Class XII [Sciences.]
admission through AIEEE
|
4years
|
Satyabhama Institution of Science & Technology, Tamil Nadu.
Website:
wwwsatyabhama.edu
|
B.Tech Biotechnology
|
Class XII admission through AIEEE
|
4 years
|
Uttar Pradesh Technical University , Institute of Engineering ,
Lucknow -226021.
Ph- 0522-732376
|
B.Tech Biotechnology& Bio. Engg.
|
10+2 with Physics, Chemistry Maths & Biology.
|
|
|
|
B.Tech Biotechnology
|
Class XII, with 50% in Physics, Chemistry and Math.
|
4 years
|
Visverswaraih Technological University, Karnataka.
Website: www.vtu.ac.in
|
B.Tech Biotechnology
|
Class XII, with Physics, Chemistry and Biology.
|
|
University of Kerela .
Website:
www.keralauniversity.edu
|
B.Tech Biotechnology
|
10+2 with 50% marks in Physics, Chemistry and Maths and 50% marks in
Maths.
|
4years
|
Vellore Institute Of Technology, Tamil Nadu.
Website: www.vit.ac.in
|
B.Tech / B.Sc Biotechnology
|
10+2 with Physics, Chemistry Maths & Biology. Entrance test.
|
4years
|
Guru Nanak Dev University , Amritsar-143005, Punjab .
Website:
www.gnduonline .org
|
1]B.Tech Biotechnology
2]B.Sc Biotechnology
|
10+2 with 55% marks in Physics Chemistry Maths & Biology.
Entrance test.
2] 10+2 sciences with 50% marks
|
4 years
|
|
|
B.Sc (vocational-course) Biotechnology
|
10+2 with 50% marks in physics, chemistry and maths.
|
3years
|
|
|
B.Sc Biotechnology
|
Class XII [Sciences.]
|
3 years
|
Amity Institute Of Biotechnology, New Delhi
Website:www.amity.edu
|
B.Sc Biotechnology
|
10+2 with 50% marks and Biology as a subject. Entrance test.
|
3years
|
|
|
B.Sc Biotechnology
|
Class XII [Sciences.]
|
3years
|
Banasthali Vidyapeeth. P.O. Banasthali Vidyapeeth. -304022
Website:
www.bansthali.org
|
B.Sc/B.Sc(Hon) Biotechnology
|
Class XII [Sciences.]
|
3years.
|
Biotechnology Courses in India after 12th
- Bachelor of Engineering in
Biotechnology
- Bachelor of Science in
Advanced Zoology & Biotechnology
- Bachelor of Science in
Applied Biotechnology
- Bachelor of Science in
Biotechnology
- Bachelor of Science
(Honours) in Biotechnology
- Bachelor of Science in
Medical Biotechnology
- Bachelor of Science in
Zoology and Animal Biotechnology
- Bachelor of Science + Master
of Science in Biotechnology
- Bachelor of Techonology in
Bioprocess Technology
- Bachelor of Techonology in
Biotechnology
- Bachelor of Techonology in
Industrial Microbiology
- Bachelor of Techonology in
Molecular & Cellular Engineering
- B.Tech. + M.Tech.
(Biotechnology)
- Bachelor of Techonology in
Biotechnology
- Advanced Diploma Course in
Biotechnology
- Diploma in Biotechnology
Engineering
- Certificate Course in
Biotechnology
- Certificate Course in
Advance Biotechnology
- Certificate in Biotechnology
and Plant Tissue Culture
- Post M.D. Certificate Course
in Biotechnology
Biotechnology Courses Abroad after 12th
- Bachelor of Science (Hons)
in Biotechnology (Applied Molecular Biology)
- Bachelor of Science (Hons)
in Medical Biotechnology
- Bachelor of Biotechnology
- Bachelor of Applied Science
(Biotechnology)
- Bachelor Degree in Resource
Biotechnology
- Bachelor of Biotechnology
and Innovation
- Bachelor of Applied Science
(BAppSc) Majoring in Molecular Biotechnology
- Bachelor of Science (BSc)
Majoring in Plant Biotechnology
- Bachelor of Science in
Chemical Engineering with Biotechnology Specialization
- Bachelor of Biomedicine
(Biotechnology)
- Bachelor of Science in
Biological Engineering - Biotechnology Engineering Concentration
- Bachelor of Medical Science
(Biotechnology)
- Bachelor of Biomolecular
Science - Environmental Biotechnology
- Bachelor of Technology in
Biotechnology
- Bachelor of Science in Agricultural
Biotechnology and Biochemistry
- Bachelor of Applied Arts and
Sciences in Biotechnology
- Bachelor in Applied Sciences
with Islamic Studies (Biotechnology)
- Diploma of Laboratory
Technology (Biotechnology)
- Graduate Diploma in
Technology
- Diploma in Biotechnology
- Diploma in Molecular
Biotechnology
- Certificate in Food
Biotechnology
- Diploma of Health Science in
Molecular Genetics and Biotechnology
Admission to most of the courses will be based on marks obtained in 12th
class examination. Admission details can be collected from the web portal of
the University that offers the particular course.