Cells in the body have specific purposes, but stem
cells are cells that do not yet have a specific role and can become almost any
cell that is required.
Stem cells are
undifferentiated cells that can turn into specific cells, as the body needs
them.
Scientists and doctors are interested in stem cells
as they help to explain how some functions of the body work, and how they
sometimes go wrong.
Stem cells also show promise for treating some diseases
that currently have no cure.
Stem cells originate from two main sources: adult body tissues and embryos.
Types
of stem cells:
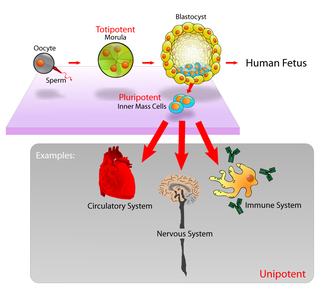
Totipotent:
These stem cells can differentiate into all possible cell types. The first few
cells that appear as the zygote starts to divide are totipotent.
Pluripotent:
These cells can turn into almost any cell. Cells from the early embryo are
pluripotent.
Multipotent:
These cells can differentiate into a closely related family of cells. Adult
hematopoietic stem cells, for example, can become red and white blood cells or
platelets.
Unipotent:
These can only produce cells of one kind, which is their own type. However,
they are still stem cells because they can renew themselves. Examples include
adult muscle stemcells.
Embryonic stem cells are considered pluripotent
instead of totipotent because they cannot become part of the extra-embryonic
membranes or the placenta.

No comments:
Post a Comment