Amino acids are organic compounds that contain amine (–NH2) and carboxyl (–COOH) functional groups, along with a side chain (R group) specific to each amino acid.[1][2] The key elements of an amino acid are carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), and nitrogen (N), although other elements are found in the side chains of certain amino acids.
Structure of Amino acids
- All 20 of the common amino acids are alpha-amino acids. They contain a carboxyl group, an amino group, and a side chain (R group), all attached to the α-carbon.

Exceptions are:
- Glycine, which does not have a side chain. Its α-carbon contains two hydrogens.
- Proline, in which the nitrogen is part of a ring.
- Thus, each amino acid has an amine group at one end and an acid group at the other and a distinctive side chain. The backbone is the same for all amino acids while the side chain differs from one amino acid to the next.
- All of the 20 amino acids except glycine are of the L-configuration, as for all but one amino acid the α-carbon is an asymmetric carbon. Because glycine does not contain an asymmetric carbon atom, it is not optically active and, thus, it is neither D nor L.
Classification of amino acids on the basis of R-group
- Nonpolar, Aliphatic amino acids: The R groups in this class of amino acids are nonpolar and hydrophobic. Glycine, Alanine, Valine, leucine, Isoleucine, Methionine, Proline.
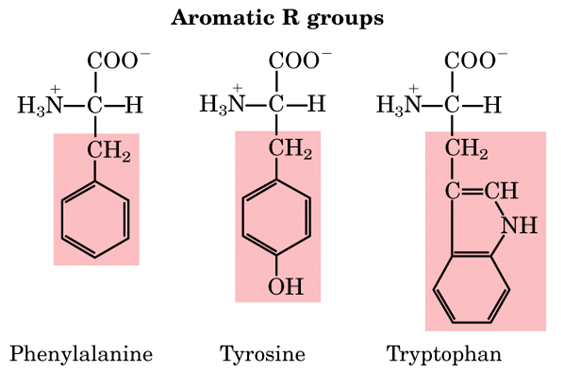
- Aromatic amino acids: Phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan, with their aromatic side chains, are relatively nonpolar (hydrophobic). All can participate in hydrophobic interactions.
- Polar, Uncharged amino acids: The R groups of these amino acids are more soluble in water, or more hydrophilic, than those of the nonpolar amino acids, because they contain functional groups that form hydrogen bonds with water. This class of amino acids includes serine, threonine, cysteine, asparagine, and glutamine.
- Acidic amino acids: Amino acids in which R-group is acidic or negatively charged. Glutamic acid and Aspartic acid
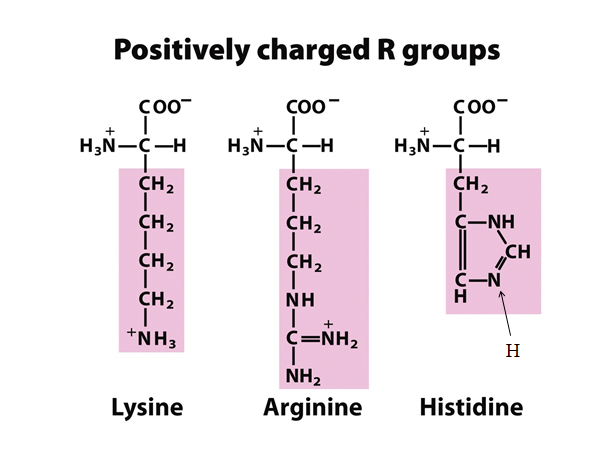
- Basic amino acids: Amino acids in which R-group is basic or positively charged. Lysine, Arginine, Histidine
Nonpolar, Aliphatic amino acids:

Negatively charged amino acids



No comments:
Post a Comment