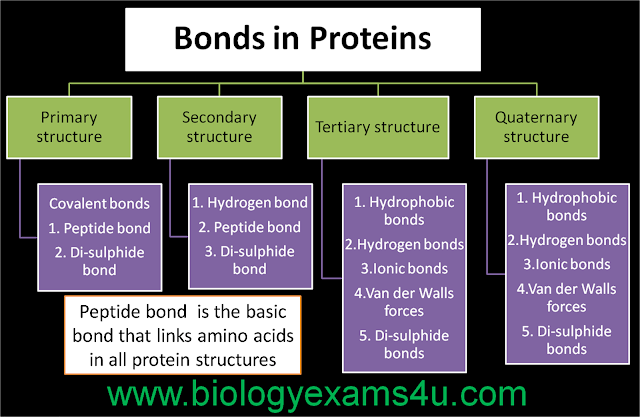
A noncovalent bond is a type of chemical bond that typically bond between macromolecules. They do not involve sharing a pair of electrons. Noncovalent bonds are used to bond large molecules such as proteins and nucleic acids.
There are four main types of noncovalent bonds in biological systems: hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, van der Waals interactions, and hydrophobic bonds.
The strongest type of non-covalent interaction is between two ionic groups of opposite charge
IONIC BONDS:
It involves interaction between oppositely charged groups of molecules. As we know that there are 20 naturally occuring aminoacids and among them 2 are negatively charged (acidic- aspartate and glutamate) while 3 are positively charged (basic - lysine, arginine and histidine). also known as salt bridges
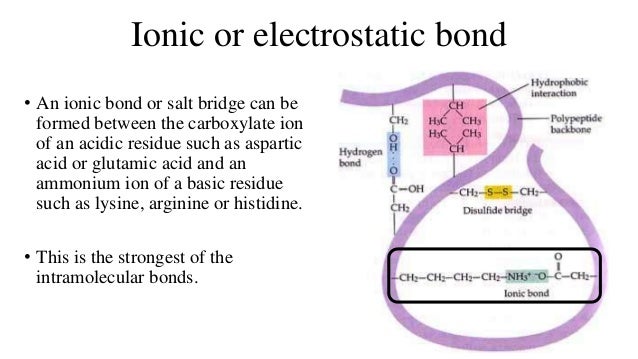
Ionic bonds are highly sensitive to pH and salt concentration means the bond strength is vastly reduced due to insulating qualities of water
HYDROGEN BONDS:
The definition of hydrogen bond is a chemical bond between the hydrogen atom and an electronegative atom as nitrogen, oxygen. In the secondary structure of proteins, hydrogen bonds form between the backbone oxygens and amide hydrogens. Hydrogen bonding confers rigidity to the protein structure and specificity to intermolecular interactions.

VAN DER WAALS FORCES:
The van der Waals force is a distance-dependent interaction between atoms or molecules. Unlike ionic or covalent bonds, these attractions do not result from a chemical electronic bond; they are comparatively weak and therefore more susceptible to disturbance. The van der Waals force quickly vanishes at longer distances between interacting molecules. These are essentially contact forces and are of little significance over larger surface area as in relation with 1/r6 where r is the inter atomic distance i.e. the distance between two atoms
HYDROPHOBIC INTERACTIONS
Hydrophobic interactions describe the relations between water and hydrophobes (low water-soluble molecules). Hydrophobes are nonpolar molecules and usually have a long chain of carbons that do not interact with water molecules. The mixing of fat and water is a good example of this particular interaction.The word hydrophobic literally means "water-fearing", and it describes the segregation of water and nonpolar substances, which maximizes hydrogen bonding between molecules of water and minimizes the area of contact between water and nonpolar molecules. For example: 
The hydrophobic effect is considered to be the major driving force for the folding of globular proteins.

No comments:
Post a Comment