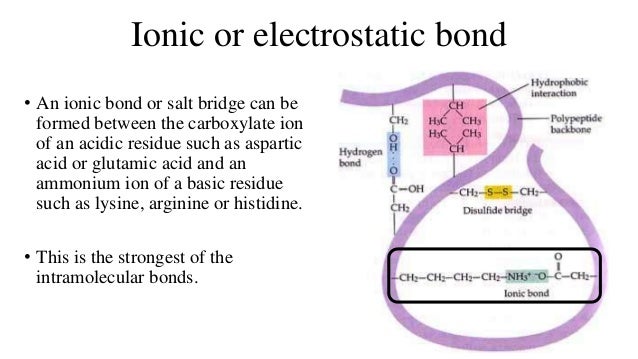
1. In RDT, what is the advantage of using vectors with polylinkers and MCS?
2. What are expression vectors?
3. What kind of promoter should be used in such vectors?
4. What do you understand by the word insertional inactivation?
5. Name any two visual methods of screening transformed bacterial cells.
6. Why the sequence we get from autoradigram is complementary to the original sequencde?
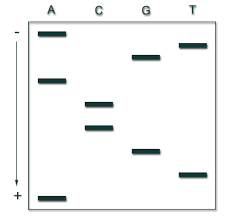
7. In the following DNA fingerprinting gel autoradiogram, which person is most likely the father of the child?

8. For identifying the fragment TTATGCCGCGATTCATACTAT, after restriction digestion genomic DNA, which probe will you use?
a. ATGCCGCGA
b. GGCGTAAGT
c. TCATACTAT
d. TTAGCTATA
9. Write the sequence of the original DNA strand of this autoradiogram where each well is showing ddNTP utilized.
10. What do you mean by the word pallindrome?
11. Why type II R.E. are most commonly exploited in RDT?
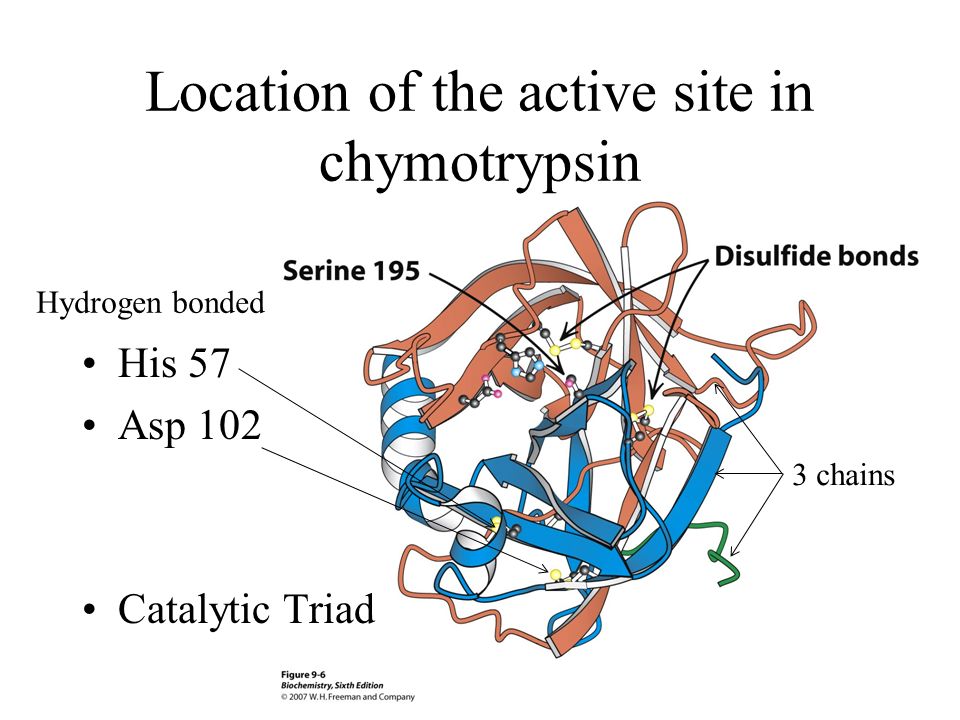
12. Name the specific enzyme shown here and its specific function.
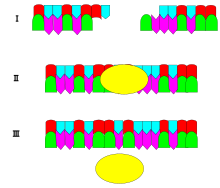
13. Name the specific enzyme shown here and its specific function.

14. Why Yep is consider as shuttle vector?
15. Following diagram shows the infection by a M13 virus to the bacterial host where it completes its lifecycle. What is the importance of ssDNA and dsDNA of M13 shown here in RDT?

16. Why E.coli is not a suitable host for expression of eukaryotic proteins?
17. Name any two plant and animal viral vectors
18. What is the function cos site of lambda DNA?
19. Which method of introduction of rDNA into host cell is depicted here"

20. How many DNa fragments will you get after completion of 12 cycles when initially 3 copies of DNA are taken as template.
21. At what temperature annealing in PCR takes place?
22. What is blotting in Southerrn Hybrdization?
23. Write any two advantages of the following library:

24. Write the principle of the techinque shown below:

25. Why cDNA lacks introns?